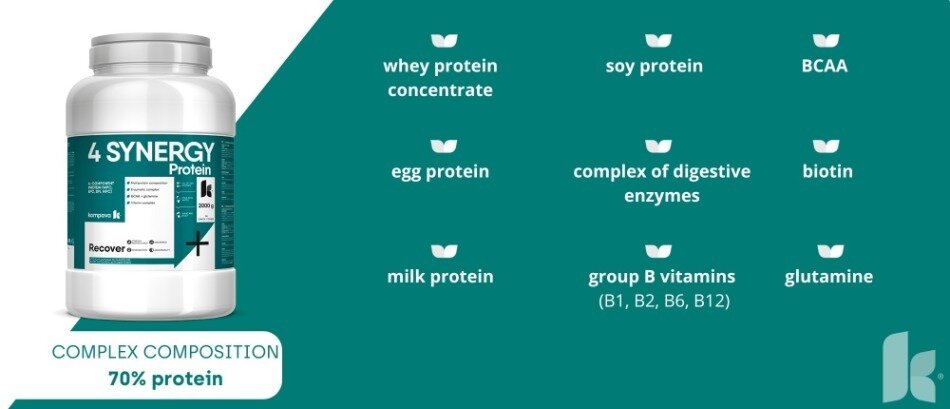
4 SYNERGY Protein is a 70%, easily digestible protein, the advantage of which is the gradual release of amino acids thanks to the content of whey, egg, milk and soy protein. This protein blend effectively supports muscle growth and regeneration, which is important for achieving optimal training results.
Milk protein provides long-term muscle support, while whey protein quickly delivers amino acids for tissue repair. Egg protein adds its essential amino acids to overall muscle growth and tissue repair. Soy protein (non-GMO), as a plant source, also contributes to building bigger muscles and recovery, and its isoflavones may be beneficial for heart health. 4 SYNERGY Protein is enriched with essential BCAA amino acids, L-glutamine and a complex of digestive enzymes, the effectiveness of which is supported by vitamins.
Thanks to the enzymes added to 4 SYNERGY Protein, the potentially unpleasant side effects of consuming an increased amount of protein, such as bloating and gas, are minimized.
Protein is one of the key nutrients you should take in after physical activity:
- proteins regenerate muscles after physical exercise,
- proteins are necessary for the production of various enzymes and hormones that control the body's metabolic processes,
- proteins restore energy reserves in the body,
- eating protein can help keep you feeling full and prevent overeating later.
4 SYNERGY Protein contains:
Whey, egg, milk and soy proteins - thanks to this combination of proteins, the protein is broken down for a longer time (4-5 hours).
- Whey protein concentrate
Whey concentrate contains a high amount of high-quality proteins and essential amino acids. It contributes to the growth and maintenance of muscle mass and the overall recovery of the body after physical activity. - Egg protein
One of the most interesting aspects of egg protein is its biological value. This value reflects the extent to which the protein is absorbed and used by the body. Egg protein has a high biological value, which indicates its effectiveness in promoting muscle growth and recovery. - Milk protein
Milk protein consists of two main components - casein and whey protein. Casein digests slowly and releases amino acids gradually, which can provide long-term muscle support. Conversely, whey protein is quickly absorbed and can be ideal for quickly supporting muscle recovery after training. Milk protein also contains a wide range of amino acids, including essential amino acids, which are necessary for muscle growth and regeneration. It has a high biological value, which means that it is able to effectively use amino acids to support protein synthesis in the body. - Soy protein
As one of the few vegetable proteins, soy protein has a complete amino profile. It contains all the essential amino acids that the body cannot create on its own and must obtain them from food. It contains phytochemicals known as isoflavones, which may have antioxidant properties and contribute to heart health. Soy protein can also help lower blood cholesterol levels. - Complex of digestive enzymes
Digestive enzymes are biologically active molecules that play a key role in the process of digesting food.
- Reduction of digestive problems: Digestive enzymes prevent digestive problems, such as feeling heavy after a meal, flatulence or cramps.
- Better absorption of nutrients: Digestive enzymes can contribute to better absorption of nutrients, including proteins, vitamins and minerals. This will ensure that the body uses incoming nutrients more efficiently to support various body functions. - BCAA
BCAA (up to 5,18 g in one dose) is a group of three essential amino acids: valine, leucine and isoleucine. These amino acids have important roles in the body, especially in muscle tissue:
- Support of muscle regeneration: BCAAs help faster regeneration of muscle tissue after training.
- Protection of muscle mass: During endurance training or muscle activity, muscle catabolism occurs, i.e. the breakdown of muscles into energy. It is BCAAs that protect muscles from breakdown and thus from overtraining (muscle fever) and damage. - Glutamine
L-glutamine is an amino acid that has important roles in the body, especially in muscle tissue and the immune system. L-glutamine is often referred to as the "regeneration amino acid" because of its role in the repair and regeneration of muscle tissue. Furthermore, it helps to minimize muscle catabolism (decomposition of muscle tissue into energy), thus maintaining muscle mass and sports performance.Glutamine is also an important player in maintaining healthy function of the small intestine, mucosal integrity and immune response. Its sufficient supply from food is important for maintaining the overall health of the digestive system. - Group B vitamins
Vitamins of the B group (B1, B2, B6, B12) contained in protein play an important role in many biochemical processes in the body, including the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. These vitamins also have a significant impact on energy metabolism, the nervous system and the formation of red blood cells. Since sports performance is often associated with demanding physiological demands on the body, B vitamins can have a positive effect on sports performance. - Biotin
It plays a key role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. It helps convert these nutrients into energy that the body needs for various physical and metabolic processes. It is also necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system. It plays a role in the transmission of nerve impulses and supports a healthy nervous system.